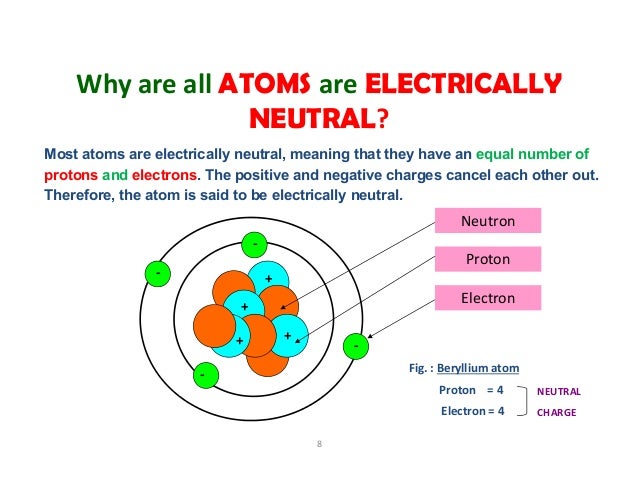
The number of electrons in an electrically-neutral atom is the same as the number of protons in the nucleus. Therefore, the number of electrons in neutral atom of Neon is 10. Each electron is influenced by the electric fields produced by the positive nuclear charge and the other (Z – 1) negative electrons in the atom. The neutral atom will have the same number of protons as the number of electrons in the ground state. To be “neutral” and atom must have the same number of protons as electrons. Usually it is the electrons that are shared, acquired or lost in chemical bonding.
How do you calculate the number of protons in a neutral atom?
1 Answer
The neutral atom will have the same number of protons as the number of electrons in the ground state.
Explanation:
To be “neutral” and atom must have the same number of protons as electrons. Usually it is the electrons that are shared, acquired or lost in chemical bonding.
The “ground state” of an atom will have a fixed number of electrons that define its chemical properties. The number of electrons can be determined from an atom’s position in the Periodic Table – or simply looked up in that table or other reference.

The neutral atom will have the same number of protons as the number of electrons in the ground state.
Related questions
Core Concepts
In this tutorial, you will learn how to calculate the number of protons, neutrons, and electrons in an atom. In addition, you will learn about the different subatomic particles. If you enjoy this tutorial, be sure to check out our others!
Covered in other articles
Vocabulary:
- Protons: Positively charged subatomic particles located in the nucleus of an atom.
- Neutrons: Neutrally charged subatomic particles located in the nucleus of an atom.
- Electrons: Negatively charged subatomic particles located in the nucleus of an atom.
- Atomic Mass: Number of neutrons and protons present.
- Atomic Number: Number of protons present in an atom.
Finding the Number of Protons
In A Neutral Atom The Number Of Protons Is Equal To The Number Of Electrons. *
The number of protons in an atom is equal to the atomic number of the element. For example, let’s use oxygen. According to the periodic table, oxygen has the atomic number eight. The atomic number is located above the element’s symbol. Since oxygen has an atomic number of eight, there must be eight protons total. Moreover, the number of protons never changes for an element.
Finding the Number of Neutrons
The number of neutrons in an atom can be calculated by subtracting the atomic number from the atomic mass. Both of these numbers can be found on the periodic table. The atomic number is listed above the symbol of the element whereas the mass number is placed below. Let’s keep using oxygen as our example. Its atomic mass is 15.999 atomic mass units (amu) and its atomic number is 8. When we subtract 8 from 15.999, we will get 8. Also, it should be noted that the number of neutrons for an element may vary. Some elements have isotopes, which have different masses and therefore different numbers of neutrons.
Finding the Number of Electrons
The number of electrons in an atom is equal to the atomic number of an element. This means the number of electrons and the number of protons in an element are equal. Therefore, the number of electrons in oxygen is 8. Moreover, since these two subatomic particles, electrons and protons, have opposite charges, they cancel out and keep the atom neutral.
Summary Table
In A Neutral Atom The Number Of Protons Is Equal To The Number Of What
Further Reading
